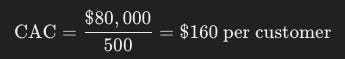Mastering the Metrics: A Deep Dive into Customer Acquisition Cost
Unlocking the Secrets to Smarter Spending and Strategic Growth in Today’s Market
Welcome to the latest edition of the HealthVC newsletter. Today, we're diving deep into the pivotal metric of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). Understanding CAC is essential for any business aiming to thrive in a competitive landscape. In this issue, we explore the nuances of CAC, including its calculation, industry benchmarks, and effective strategies for optimization. Whether you're looking to refine your marketing approach, enhance budgeting accuracy, or simply gain a clearer understanding of acquiring and retaining customers cost-effectively, this newsletter is your comprehensive guide. Join us as we unravel the secrets to mastering CAC and boosting your business's financial health.
Introduction to Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Definition of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) represents a critical financial metric used by businesses to quantify the total average cost spent on acquiring a new customer. This figure encompasses all associated expenses required to convert potential leads into customers within a specific timeframe. Essentially, CAC is calculated by summing up the total marketing and sales expenditures over a given period and dividing that by the number of customers acquired during the same period.
Overview of Its Significance in Modern Business Practices
CAC is a pivotal metric in the landscape of modern business practices for several reasons:
Strategic Planning and Budgeting:
Resource Allocation: CAC helps companies determine how much budget to allocate to their marketing and sales efforts. Understanding CAC allows businesses to strategize more effectively, allocating resources to channels and campaigns that yield the best return on investment (ROI).
Financial Forecasting: By calculating CAC, businesses can forecast future expenses related to customer acquisition, which is crucial for long-term financial planning and sustainability.
Performance Measurement:
Marketing Efficiency: CAC is often used as a benchmark to gauge the effectiveness of marketing strategies. A lower CAC indicates that a company is acquiring customers more efficiently, maximizing the impact of its marketing spend.
Sales Team Effectiveness: Besides marketing, CAC also measures the performance of sales teams. It assesses how well sales personnel convert prospects into actual customers, reflecting their efficiency and the effectiveness of sales processes and training.
Investment Attractiveness:
Investor Consideration: Potential investors often look at CAC to assess the efficiency of a company's growth model. A lower CAC is typically attractive to investors as it suggests the company has a sustainable growth strategy and can scale without proportionately increasing its acquisition costs.
Company Valuation: CAC directly impacts the valuation of a company. Businesses with optimized CAC are often valued higher because they demonstrate a capability to grow their customer base without exorbitant spending, ensuring better profitability and ROI.
Competitive Analysis:
Market Positioning: Understanding CAC in relation to competitors can help a company position itself more effectively in the market. Businesses often use CAC to benchmark against industry averages, which can inform strategic decisions such as pricing, marketing, and product development.
Customer Value Maximization: By analyzing CAC, companies can identify the most profitable customer segments and tailor their marketing efforts to target these groups more effectively, thus enhancing overall market competitiveness.
CAC is not just a metric of expenditure but a reflection of a company's strategic alignment in terms of customer relationship management, marketing efficiency, and overall business health. It plays an integral role in driving sustainable growth and profitability by ensuring that the cost of acquiring new customers aligns with their lifetime value. As such, understanding and optimizing CAC is paramount in modern business practices, enabling businesses to thrive in competitive environments and adapt to ever-changing market dynamics.
Components of Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a comprehensive metric that includes various direct and indirect costs associated with acquiring new customers. Understanding these components is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their spending and improve return on investment (ROI). Here, we explore the direct and indirect costs that contribute to the total CAC and how they interact to impact a company's financial and operational strategies.
Direct Costs
Advertising:
Definition and Scope: Advertising costs are the expenses associated with creating and placing ads across various channels, including digital (social media, search engines, websites) and traditional media (television, radio, print).
Impact on CAC: These are often the most significant direct costs in customer acquisition calculations. Effective advertising strategies that clearly target the intended audience can lower CAC by increasing conversion rates.
Marketing Materials:
Definition and Scope: This includes the cost of producing physical and digital marketing materials such as brochures, flyers, banners, email campaigns, and content for inbound marketing.
Impact on CAC: While seemingly less significant per unit, the scale and frequency of these materials can accumulate substantial costs. The efficiency of these materials in terms of design, message clarity, and relevance to the target audience directly influences their effectiveness in customer conversion.
Promotional Costs:
Definition and Scope: Promotional costs involve expenses related to promotional activities such as trade shows, product demos, samples, and introductory offers or discounts.
Impact on CAC: Promotions can quickly attract large volumes of customers, potentially reducing CAC if the promotions are well-targeted and timed. However, if not managed properly, they can also lead to increased costs without corresponding returns.
Indirect Costs
Salaries of Marketing and Sales Teams:
Definition and Scope: These costs include the salaries, bonuses, and other compensation for marketing and sales personnel who are directly involved in customer acquisition activities.
Impact on CAC: The efficiency and effectiveness of the marketing and sales teams play a critical role in controlling CAC. High-performing teams can significantly reduce CAC through effective strategies and execution, whereas underperforming teams may lead to increased costs.
Overhead Associated with Marketing and Sales:
Definition and Scope: This includes the administrative and operational costs related to maintaining marketing and sales departments, such as office space, utilities, software tools, and technology support.
Impact on CAC: While these costs are less directly tied to customer acquisition, they still contribute to the overall cost environment and efficiency of the marketing and sales operations.
Integration of Costs to Form Total CAC
Understanding how these direct and indirect costs combine is essential for accurately calculating and optimizing CAC:
Comprehensive Calculation: The total CAC is derived by summing all direct and indirect costs associated with marketing and sales activities within a specific period and dividing this total by the number of customers acquired during the same period.
Strategic Implications: Businesses must strategically manage both types of costs to maintain a healthy balance between spending and customer acquisition rates. For instance, increasing advertising budgets might lower CAC if it leads to a proportionally higher number of acquired customers. Conversely, excessive promotional costs without a corresponding increase in customer base can inflate CAC.
Operational Efficiency: Reducing indirect costs, such as by streamlining marketing operations or enhancing sales team productivity through training and better tools, can also significantly impact CAC. Efficient operations ensure that the business gets the most out of every dollar spent on customer acquisition.
A detailed understanding of the components of CAC not only helps in accurate calculation but also in strategic decision-making regarding budget allocation, operational improvements, and long-term financial planning. By analyzing these components, businesses can identify areas for cost optimization and enhance the overall effectiveness of their customer acquisition strategies.
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Understanding how to calculate Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is essential for any business that invests in marketing and sales activities to attract new customers. Accurate calculation of CAC not only helps in assessing the effectiveness of these activities but also plays a crucial role in financial planning and budget management. Below, we detail the step-by-step process of calculating CAC, provide illustrative examples, and discuss the importance of this metric in a business's financial strategy.
Step-by-Step Calculation of CAC
Identify All Associated Costs:
Begin by compiling all expenses related directly to acquiring new customers over a specific period. This includes both direct and indirect costs:
Direct Costs: Advertising, marketing materials, promotions, etc.
Indirect Costs: Salaries of marketing and sales teams, overhead costs associated with these teams, etc.
Determine the Time Frame:
Select a relevant period for analysis, such as a quarter or a fiscal year. This period should reflect a typical or strategic cycle in your business operations and customer acquisition efforts.
Sum Up Total Costs:
Add up all the costs identified in the first step for the selected period. This total represents the overall investment made to attract new customers.
Count the Number of New Customers Acquired:
Calculate the total number of new customers acquired during the same period. This involves tracking new sales and ensuring they are from first-time customers.
Calculate CAC:
Divide the total costs from Step 3 by the number of new customers from Step 4. The formula is
:
Example to Illustrate the Calculation
Suppose a company spends the following in one quarter:
Advertising: $20,000
Marketing Materials: $5,000
Promotions (discounts, etc.): $10,000
Salaries (Marketing and Sales): $30,000
Overhead (related to Marketing and Sales): $15,000
Total Costs = $20,000 + $5,000 + $10,000 + $30,000 + $15,000 = $80,000
During this quarter, the company acquires 500 new customers. Thus, the CAC is calculated as:
Importance of Accurately Calculating CAC
Budgeting and Financial Planning:
Resource Allocation: Accurate CAC calculation helps businesses decide how much to budget for customer acquisition activities. Understanding the cost-effectiveness of different strategies allows for better allocation of marketing funds.
Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating CAC provides essential insights into the profitability of acquiring new customers. Businesses can assess whether the lifetime value (LTV) of the customers justifies the CAC, which is crucial for sustainable growth.
Strategic Adjustments: Regular assessment of CAC helps in tweaking marketing strategies based on their performance. If CAC is too high, a company might need to rethink its channels or tactics to find more cost-effective ways of customer acquisition.
Long-term Financial Health:
Predicting Growth: By understanding CAC, businesses can predict future growth more accurately. Lower CAC relative to LTV suggests that the business can scale sustainably.
Investor Insights: For startups and companies seeking investment, a well-calculated CAC is crucial to demonstrate to investors that the company has a viable financial model.
Mastering the calculation of Customer Acquisition Cost is not just about tracking expenses but also about optimizing business growth and ensuring financial efficiency. By regularly analyzing and adapting strategies based on CAC, businesses can enhance their marketing efficacy and improve overall financial health.
Industry Benchmarks and Comparisons
Understanding Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) requires not only internal assessments but also external comparisons. Analyzing industry benchmarks and how CAC varies across different sectors can provide valuable insights into market dynamics and competitive strategies. This section explores the average CAC across various industries, highlights sector-specific differences, and delves into the factors that influence these variations.
Overview of Average CAC Across Different Industries
CAC can vary significantly from one industry to another due to differing business models, customer behaviors, and marketing efficiencies. For instance:
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS companies often exhibit higher CAC due to the need for significant upfront investment in technology development and customer education. However, these costs are generally offset by higher lifetime value (LTV) due to recurring revenue models.
E-commerce: Online retailers may experience lower CAC compared to traditional retail due to digital marketing efficiencies and direct-to-consumer channels. E-commerce platforms can leverage targeted advertising and data analytics to efficiently acquire customers.
Financial Services: This sector can have a high CAC due to the necessity of building trust and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. Marketing efforts often require more personalized outreach and education.
Healthcare: The healthcare industry faces unique challenges that can drive up CAC, including long sales cycles, the need for detailed product explanations, and compliance with health regulations.
A generalized understanding of CAC benchmarks can be misleading without considering the nuances of each industry. For example, a tech startup may have a high CAC in its early stages as it invests heavily in customer acquisition but expects this cost to decrease as brand awareness and customer referrals grow.
Discussion on Sector-Specific Differences in CAC
Retail Sector: Traditional retail often involves higher physical overhead, which can contribute to a higher CAC. Promotions and physical advertising are common, but the switch to digital platforms is helping lower these costs.
Tech Sector: Technology companies, particularly in the digital and SaaS space, might have high initial CAC due to the need for significant market education and software development. However, the scalability of digital products allows for rapid growth and potentially lower CAC over time.
Service Sector: Services that require high-touch customer interactions, such as consulting and professional services, often have higher CAC due to the need for personalized marketing and the longer timeframe required to close sales.
Analysis of Factors Influencing These Differences
Several factors contribute to the differences in CAC across industries:
Customer Lifecycle and Retention: Industries with longer customer lifecycles, like automotive or real estate, may have higher CAC but also higher customer lifetime value. The investment in acquiring a customer is justified by the extended duration of revenue generation.
Market Saturation and Competition: Highly competitive markets, such as the tech industry, often see elevated CAC as companies vie for market share and customer attention. More competition generally leads to higher marketing spend, which drives up CAC.
Product Complexity and Education Needs: Products that require significant customer education or demonstrate complex value propositions typically incur higher CAC. Industries like healthcare technology or financial services need to invest heavily in educating their market, which increases initial acquisition costs.
Regulatory Environment: Industries subject to stringent regulations, such as healthcare and financial services, need to ensure compliance in their marketing and customer interaction processes, often leading to higher costs.
Marketing Channels and Strategies: The effectiveness of different marketing channels also plays a critical role in determining CAC. Digital-first industries, such as e-commerce and digital services, can leverage online marketing tools efficiently, potentially lowering CAC compared to industries reliant on traditional marketing channels.
By comparing industry-specific benchmarks and understanding the underlying factors that influence these costs, companies can better strategize their customer acquisition approaches. This analysis not only helps in optimizing marketing budgets but also in aligning strategic objectives with industry standards, ensuring competitive advantage and financial sustainability.
Strategies to Optimize Customer Acquisition Cost
Effectively managing and optimizing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is pivotal for enhancing a company's profitability and growth. This section explores various strategies to lower CAC, the significant role digital marketing and social media play in reducing these costs, and case studies highlighting successful CAC optimization efforts.
Effective Marketing Strategies to Lower CAC
Reducing CAC starts with implementing targeted marketing strategies that not only reach the right audience but also convert engagements into sales efficiently. Key strategies include:
Targeting and Segmentation: Utilize data analytics to precisely target marketing efforts towards demographics most likely to convert. Segmenting the audience based on behaviors, preferences, and previous interactions can significantly increase conversion rates, thereby lowering CAC.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools: Implementing advanced CRM tools can help track customer interactions and optimize marketing campaigns. These tools facilitate better targeting, personalize customer communications, and enhance customer engagement, which can lead to higher conversion rates and reduced acquisition costs.
Performance Marketing: Focus on performance-based marketing channels where payment is based on the outcome of the marketing activity, such as pay-per-click (PPC), affiliate marketing, and cost-per-acquisition (CPA) models. This approach ensures that marketing spend is directly correlated with actual customer acquisitions, optimizing the use of the marketing budget.
Content Marketing: Develop high-quality, informative content that addresses customer needs and questions. Effective content marketing not only helps in attracting potential customers but also builds trust, which can lead to higher conversion rates at lower costs.
Referral Programs: Encourage existing customers to refer new customers through referral programs that offer incentives for both referrers and new customers. This word-of-mouth strategy can significantly reduce CAC by leveraging the networks of current satisfied customers.
Role of Digital Marketing and Social Media in Reducing CAC
Digital marketing and social media play a crucial role in reducing CAC by allowing for more precise targeting, real-time optimization, and direct customer engagement:
Social Media Advertising: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter provide advanced targeting options based on user demographics, interests, and behaviors, enabling businesses to reach their ideal customer profile more directly and cost-effectively.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and Search Engine Marketing (SEM): By optimizing content for search engines, businesses can increase their visibility when potential customers are actively searching for related products or services, often resulting in lower CAC compared to traditional advertising methods.
Email Marketing: Segmenting email lists and personalizing email messages can dramatically improve conversion rates. Email marketing remains one of the most cost-effective strategies due to its direct approach and personalization capabilities.
Retargeting Campaigns: Implementing retargeting strategies can help capture potential customers who did not convert on their first visit to a website. Retargeting keeps track of these individuals and serves targeted ads to them, thereby increasing the likelihood of conversion at a relatively low cost.
Case Studies of Successful CAC Optimization
Several businesses have successfully optimized their CAC through innovative strategies:
Dropbox: Dropbox effectively reduced its CAC through a referral program that offered extra storage space to both the referrer and the new user. This strategy leveraged existing customer networks and significantly increased user acquisition without corresponding increases in marketing spend.
Warby Parker: By offering home try-on for glasses, Warby Parker increased conversions while maintaining a low CAC. This unique approach reduced the hesitance associated with buying eyewear online, enhancing customer experience and satisfaction.
Airbnb: Airbnb reduced its CAC by leveraging high-quality content and SEO strategies to attract users organically. By focusing on unique accommodations and local experiences, Airbnb’s content appealed directly to its target audience, driving traffic and conversions through organic search.
Optimizing CAC involves a blend of targeted marketing strategies, leveraging modern digital marketing tools, and continuously refining approaches based on data-driven insights. Companies that succeed in these areas not only reduce their CAC but also improve overall marketing efficiency, leading to sustained business growth and profitability.
Relationship between Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Understanding the relationship between Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is crucial for businesses aiming to maximize their profitability and ensure long-term sustainability. This section explores the definition of CLV, its importance, how it influences CAC, and strategies for balancing the two metrics effectively.
Definition of CLV and Its Importance
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a metric that estimates the total revenue a business can reasonably expect from a single customer account throughout their relationship with the company. It factors in the revenue generated from a customer over time, minus the costs associated with acquiring and serving them.
The importance of CLV lies in its ability to quantify the long-term value of customers, helping businesses to make informed decisions about how much money they should invest in acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones. CLV is particularly critical because it shifts the focus from short-term gains to long-term profitability and customer relationships. By understanding and optimizing CLV, companies can:
Allocate resources more efficiently: Knowing the lifetime value of customers allows businesses to allocate marketing and operational resources more strategically.
Enhance customer segmentation: CLV helps in identifying high-value customers, which allows for more targeted and personalized marketing efforts.
Improve return on investment (ROI): By focusing on customers with higher CLVs, companies can optimize their ROI on marketing campaigns.
How Understanding CLV Can Influence CAC
A deep understanding of CLV can significantly influence how a business approaches CAC. If the lifetime value of a customer is high, a company can justify a higher CAC because the return on that investment is substantial over time. Conversely, if CLV is low, businesses need to find ways to reduce CAC to maintain profitability.
Incorporating CLV into CAC considerations enables businesses to:
Set appropriate CAC targets: Businesses can set benchmark CAC based on the CLV of different customer segments. This ensures that acquisition costs are always proportionate to the expected return from customers.
Focus on quality over quantity: Instead of merely increasing the customer base, businesses can focus on acquiring customers who promise higher lifetime values.
Adjust marketing strategies: With a clear understanding of CLV, companies can tailor their marketing strategies to attract and retain high-value customers, potentially increasing the overall efficiency of their marketing spend.
Strategies to Balance CAC with CLV
Balancing CAC with CLV is vital for sustaining business growth and profitability. Here are some strategies businesses can employ to maintain this balance:
Enhance Customer Retention: Since increasing customer retention rates can significantly boost CLV, focusing on customer service and satisfaction can naturally balance out the CAC. Implementing loyalty programs, providing exceptional post-purchase support, and regular customer engagement can enhance retention.
Optimize Marketing Spend: Use data analytics to identify which marketing channels yield customers with the highest CLV and allocate budgets accordingly. Reducing spend on low-performing channels will decrease CAC and improve overall marketing efficiency.
Improve Product and Service Offerings: Continuously enhancing product and service offerings based on customer feedback and market trends can increase CLV. When customers perceive greater value in a company's offerings, their lifetime value increases, which can justify a higher CAC if necessary.
Use Predictive Analytics: Employ predictive analytics to forecast CLV based on customer behavior patterns. This allows businesses to adjust their acquisition strategies proactively, focusing on acquiring customers whose behaviors indicate a high potential CLV.
Regularly Review and Adjust Strategies: Market conditions and customer behaviors change, so it's essential to regularly review and adjust CAC and CLV strategies. This ensures that the business remains agile and can respond to changes in customer preferences and market dynamics effectively.
Understanding and effectively managing the relationship between CAC and CLV is critical for maximizing business profitability. By focusing on strategies that enhance CLV, companies can afford to invest in higher CAC when necessary, ensuring that each customer acquired contributes positively to the long-term financial health of the business.
Retaining Customers to Offset Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Retaining existing customers is a critical strategy for offsetting the often substantial costs associated with acquiring new customers. This section delves into why customer retention is vital concerning CAC, explores various strategies to improve customer service that enhance retention, and provides examples of companies that have successfully implemented these strategies to positively impact their CAC.
Importance of Customer Retention in Relation to CAC
Customer retention directly influences the long-term profitability and sustainability of a business. It is significantly cheaper to keep an existing customer than to acquire a new one, with estimates suggesting that attracting a new customer can be five to 25 times more expensive than retaining an existing one. Here’s why focusing on customer retention is crucial for managing CAC effectively:
Lower Marketing Costs: Retained customers require less investment in terms of marketing compared to the effort and resources needed to attract new customers.
Increased Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Retained customers tend to buy more over time and often become more profitable the longer they stay with a company.
Better Word-of-Mouth and Referrals: Satisfied, loyal customers are more likely to recommend a brand to others, effectively reducing the need for extensive marketing efforts and subsequently lowering CAC.
Stability and Predictable Revenue Streams: A solid base of loyal customers provides predictable revenue streams and financial stability, allowing businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and plan with greater confidence.
Strategies for Improving Customer Service to Enhance Retention
Improving customer service is a proven strategy for enhancing customer retention. Below are several effective approaches:
Training and Empowerment of Customer Service Teams: Ensure that customer service teams are well-trained and empowered to solve customer issues quickly and effectively. This might include training in communication skills, problem-solving, product knowledge, and handling difficult situations.
Personalization of Customer Interactions: Use data analytics to personalize interactions and communications. Personalization can range from addressing customers by their names in emails to recommending products based on past purchases.
Quick Response Times: Rapid responses to customer inquiries and issues are crucial. Implementing live chat support and ensuring that customer service hotlines are adequately staffed can dramatically improve customer satisfaction and retention.
Proactive Customer Service: Reach out to customers before they come to you with problems. This can include checking in to ensure they are satisfied with their purchase or updating them about how to get the most out of their products.
Loyalty Programs: Develop loyalty programs that reward customers for repeat purchases or referrals. These programs not only encourage additional sales but also foster a sense of belonging and appreciation.
Examples of Companies with Successful Retention Strategies Impacting CAC
Amazon Prime: Amazon’s Prime membership not only enhances customer loyalty through various perks such as free shipping, exclusive deals, and streaming video services but also effectively reduces CAC by turning one-time buyers into repeat customers.
Apple: Known for its high customer retention rates, Apple succeeds through a combination of exceptional product quality, excellent customer service, and a strong ecosystem of products and services that encourage loyalty.
Zappos: Zappos sets a high industry standard for customer service with a 365-day return policy and a highly responsive customer service team, which has led to high levels of customer retention and referrals, significantly impacting their CAC.
Netflix: Netflix maintains high retention rates through quality content, a personalized viewing experience, and excellent customer service. This strategy helps to keep CAC in check by stabilizing and expanding its customer base.
Enhancing customer retention is a crucial strategy for managing and offsetting CAC. By investing in quality customer service and retention strategies, companies can not only reduce their overall marketing expenditures but also build a more loyal and profitable customer base. The success of companies like Amazon, Apple, Zappos, and Netflix underscores the effectiveness of these strategies in reducing CAC and boosting profitability.
Technological Tools to Measure and Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
In the digital age, leveraging technology to measure and reduce Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is not just an option but a necessity for businesses aiming to optimize their marketing strategies and improve overall efficiency. This section explores the role of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems and other technological tools in tracking and minimizing CAC, how these technologies can streamline customer acquisition processes, and provides real-world examples of successful technology implementations.
Introduction to CRM and Other Tools to Track and Optimize CAC
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are integral to modern business strategies, designed to manage a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. By integrating data from various communication channels, including a company's website, telephone, email, live chat, and social media, CRMs help businesses learn more about their target audiences and how to best cater to their needs, thereby potentially reducing CAC.
Beyond CRM, there are several other technological tools and platforms that help in measuring and reducing CAC:
Marketing Automation Platforms: These tools automate repetitive tasks such as emails, social media posting, and other website actions. They help in nurturing leads efficiently, thereby reducing the manpower costs associated with these tasks.
Analytics and Data Management Platforms: Tools like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and specialized ad tech platforms provide deep insights into customer behavior and campaign performance, allowing for refined marketing strategies that target the most profitable customer segments.
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): These platforms create a comprehensive and persistent customer database that is accessible to other systems. This data can be used to optimize marketing efforts and streamline customer acquisition processes.
How Technology Can Reduce Costs and Streamline Customer Acquisition Processes
Technology can significantly reduce CAC by streamlining acquisition processes, improving targeting, and enhancing the efficiency of marketing campaigns:
Enhanced Targeting and Segmentation: Advanced analytics tools enable businesses to segment their audiences more effectively and target them with personalized marketing campaigns that are more likely to convert, thereby reducing wastage of resources.
Automation of Marketing Processes: Automation tools can manage early-stage customer interactions, lead qualification, and initial follow-ups, which reduces the need for direct human intervention and lowers costs.
Improved Conversion Rates: By leveraging technology to test different aspects of marketing campaigns (like A/B testing tools), companies can discover the most effective messages and channels, improving conversion rates and reducing the overall CAC.
Case Studies of Technology Implementation Reducing CAC
Several companies have successfully implemented technology to reduce their customer acquisition costs:
Zappos: By using advanced data analytics to understand customer preferences and improve service delivery, Zappos has significantly enhanced customer satisfaction and retention. Their use of CRM systems to manage customer interactions has helped them in providing personalized service, which not only retains customers but also attracts new ones through word-of-mouth, thereby reducing their CAC.
Netflix: Netflix uses big data and analytics to understand viewer preferences to not just retain customers but also to acquire new ones by predicting what content will be popular and where. Their targeted advertising strategies based on viewing data significantly reduce CAC by improving conversion rates on their marketing campaigns.
Airbnb: Airbnb utilizes a combination of CRM and data analytics tools to optimize its listings and pricing strategies, which improves user experience and increases bookings. Their strategic use of social media and email marketing automation has allowed them to acquire new customers more efficiently and at a lower cost.
Technology plays a pivotal role in measuring and reducing Customer Acquisition Cost by enabling more precise targeting, automating repetitive tasks, and providing actionable insights to refine marketing strategies. Companies that embrace these technological tools are better positioned to optimize their marketing budgets, reduce CAC, and ultimately improve their profitability.
Future Trends in Customer Acquisition Costs
As businesses continuously seek more effective strategies to attract new customers, understanding the future landscape of Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC) becomes crucial. This section explores the likely evolution of CAC in response to changing consumer behaviors and advancements in technology, particularly focusing on the roles of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Additionally, it discusses the necessary preparations businesses must consider to navigate future challenges in customer acquisition effectively.
Predictions on How CAC Might Evolve with Changes in Consumer Behavior and Technology
Consumer behavior has always been a dynamic force driving marketing strategies, but with the rapid advancement of technology, these behaviors are changing at an unprecedented pace. Increased digital connectivity has led consumers to demand more personalized, seamless experiences across various platforms. As a result, businesses are expected to invest more in omnichannel strategies and advanced targeting technologies, potentially increasing the short-term CAC but aiming for a higher return through improved customer loyalty and lifetime value.
Moreover, as privacy regulations become stricter, and consumers become more protective of their data, traditional data collection methods will need to evolve. This shift could increase the CAC as businesses strive to develop new methods for gathering and utilizing consumer insights without infringing on privacy.
Impact of Emerging Technologies like AI and Machine Learning on CAC
AI and machine learning are set to transform how businesses approach customer acquisition. By harnessing these technologies, companies can:
Predict Consumer Behavior: Advanced algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict consumer purchasing patterns and preferences, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
Optimize Marketing Spend: AI can help optimize advertising spend by automatically adjusting bids and reallocating budgets in real-time to the most effective channels and customer segments.
Enhance Personalization: Machine learning can tailor marketing messages and offers to individual preferences, significantly improving conversion rates and reducing overall CAC.
These technologies not only promise to make customer acquisition more efficient but also more cost-effective, potentially lowering CAC while simultaneously driving up conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Preparing for Future Challenges in Customer Acquisition
To prepare for future challenges in customer acquisition, businesses should focus on the following strategic areas:
Invest in Technology: Stay ahead of technology trends by investing in AI, machine learning, and data analytics tools that can provide deeper insights into customer behavior and improve the efficiency of marketing campaigns.
Focus on Customer Experience: As CAC potentially rises, enhancing customer experience becomes crucial. Providing superior service and seamless interactions across all channels can help improve retention and increase customer lifetime value, offsetting higher acquisition costs.
Adapt to Regulatory Changes: Keep abreast of changes in data privacy laws and adjust data collection and marketing practices accordingly to maintain consumer trust and compliance.
Conclusion
This discussion on Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) has covered its definition, calculation, importance, and the strategies for optimizing it within various business contexts. By understanding the components that contribute to CAC and employing strategies to optimize these expenses, companies can effectively enhance their profitability and sustainability.
As we look towards the future, it's evident that CAC will continue to be influenced significantly by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. The integration of AI and machine learning not only promises to reduce CAC but also to enhance the effectiveness of customer acquisition strategies. However, businesses must also prepare to face new challenges, particularly those associated with privacy concerns and the evolving regulatory landscape.
In conclusion, as the landscape of customer acquisition continues to evolve, the ability to adapt and optimize CAC remains a critical component of business success. Companies that proactively embrace new technologies and refine their strategies to align with consumer expectations will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
Now let’s take a look at the latest funding rounds, and M&A deals as well as the latest articles and videos worth reading and watching.